Agriculture?
The loss of indigenous seeds and the world’s biodiversity and fertile soils is a mortal threat to our future existence. As per the scientists’ knowledge, current soil destruction rates include desertification, decarbonization, and chemical pollution. Within 50 years, we can not only cause serious harm to public health but as a qualitatively deteriorating food supply, lack of nutrition, and there will be loss. We can get essential trace minerals, but we will no longer have enough arable top soil to feed ourselves without regenerating and protecting the soils. That is our 4 billion acres of agricultural land, 10 billion acres of forest land, and 8 billion acres of pasture. It would be impossible to feed the world, keep global warming below 2°C, or prevent damage to biodiversity.
Regenerative Agriculture Objectives

We regenerate in agriculture to fulfil the 4 objectives to make farming activities great.
Thestady
1. Biodiversity
It aims to increase animal and plant biodiversity below and above the ground. For example, It helps restore critical ecosystems by planting a million trees on the farms and landscapes, such as shade and fruit trees in cocoa-growing areas. The aim is to contribute to improved soil nutrient cycles and climate change resilience.
2. Suitable Soil
Regenerative Agriculture meaning is helping to enhance agricultural practices that help increase soil organic matter and also helps protect soil health by launching our Farmer Connect program, which works with 5,00,000 farmers and 1,50,000 suppliers works closely with local communities.
3. Water Capacity
Regenerative Agriculture’s objective is to reduce agricultural chemical inputs and also optimise organic fertilisers, irrigation and pest control techniques. Conservation of water resources and protecting natural water qualities are essential for regeneration in agriculture. We recognize the need to play our part in helping to save, restore and renew water sources.
4. Dairy
Regenerative Agriculture’s goal is to integrate livestock and optimise grazing into agricultural systems when possible. Regenerative dairy farming is also at the heart of our efforts to turn dairy into a net-zero industry. This work includes silvopasture – where trees are introduced into areas used for livestock grazing. And there is mixed farming of crops and livestock, cover crops to protect the soil, and manure management to improve.
What Does Regenerative Agriculture Work?
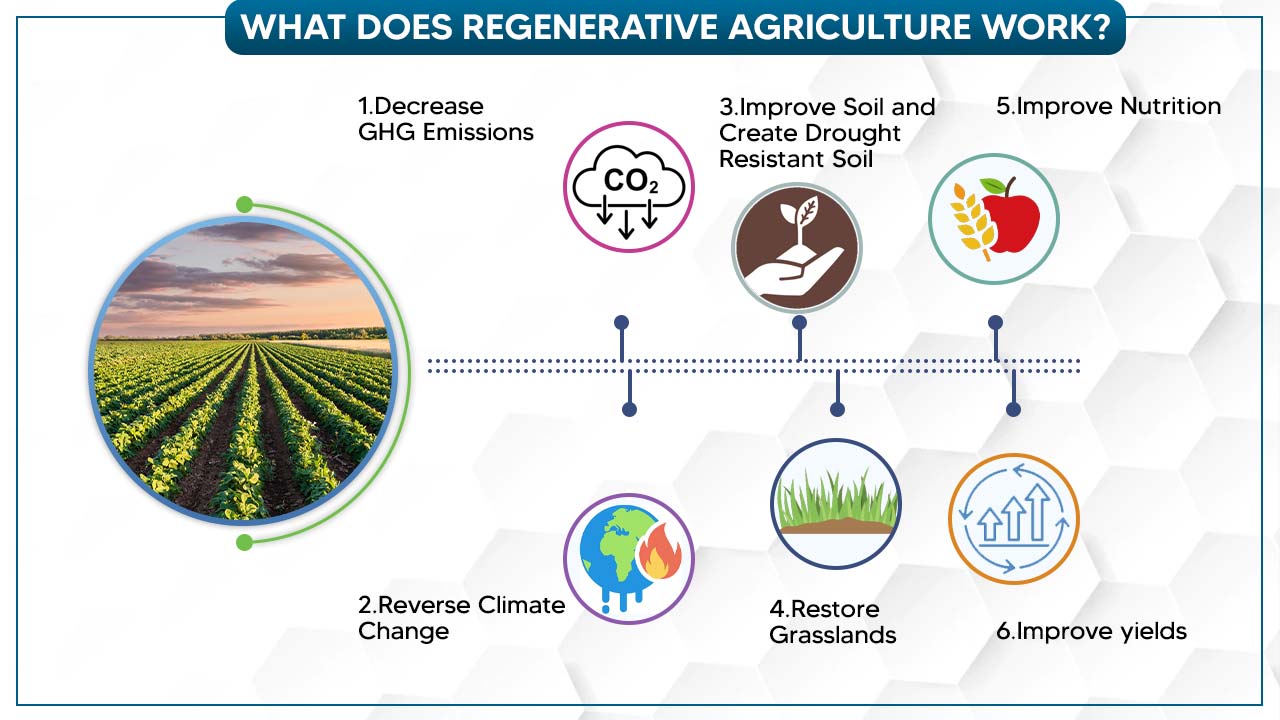
These are the regenerative agriculture principles to make farming better in India.
1. Decrease GHG Emissions
A new food system could be a major driver for addressing regenerative agriculture and also for climate change. The current industrialised food system accounts for 44 to 57% of all global greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Reverse Climate Change
We are at a critical moment in the history of species, as man-made climate changes threaten humanity’s security on Earth. But there is a regenerative agriculture technique for large-scale planetary geoengineering that is available for wide dissemination. Moreover, it costs less and is well suited to local contexts worldwide.
3. Improve Soil and Create Drought-Resistant Soil
Regenerative organic matter affects the soil’s physical and chemical properties and overall health. Properties influenced by organic matter include moisture holding capacity, soil structure, diversity and activity of soil organisms, both harmful and beneficial to crop production, and nutrient availability. In addition, regenerative organic agriculture matter to the soil enhances the water holding capacity of the soil.
4. Restore Grasslands
Grasslands are one-third of the Earth’s surface, of which 70% have been eroded. You can restore them by using holistic planned grazing. Nowadays, the area of grasslands has decreased dramatically, especially in industrialised countries. Therefore, grassland restoration is widely implemented to preserve biodiversity and enhance the naturalness of the landscape.
5. Improve Nutrition
Nutritionists are increasingly stressing the need for agro-ecosystems to ensure a more diverse nutrient production of agricultural systems. However, the food grown by farmers under regenerative practices contained more magnesium, potassium, calcium and zinc; more vitamins, including B1, B12 etc.
6. Improve yields
In cases of extreme weather/climate change and improving the soil, yields on regenerative agriculture farms are higher than on conventional farms. As a result, fertility and soil health improves, evidenced by healthier crops and improved yields.
How does Regenerative Agriculture work?
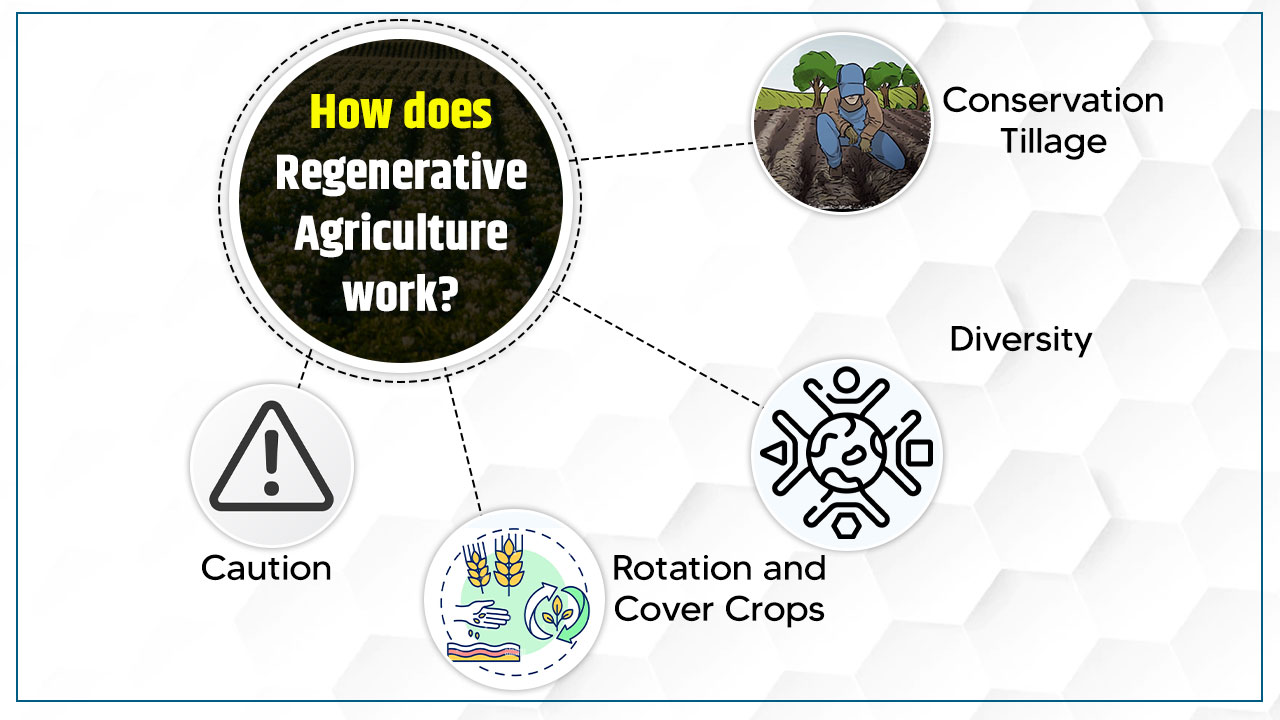
1. Conservation Tillage
Ploughing destroys the soil and releases large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. They can also result in bare or compacted soil, creating a hostile environment for important soil microbes. By adopting little or no tillage practices, farmers reduce soil physical disturbances and increase soil organic matter levels over time, creating a healthier, more resilient environment for plants to thrive.
2. Diversity
Separate plants release different carbohydrates through their roots, and different microbes feed on these carbs and return all kinds of different nutrients to the plant and the soil. So by increasing the plant diversity of their local regenerative farms, farmers help create rich and nutrient-rich soils that lead to more productive yields.
3. Rotation and Cover Crops
Exposure to the elements will lead to soil erosion, and the nutrients needed for successful plant growth will either wash away or dry up. At the same time, planting the same plant in the same location can create a build-up of deficiency and some nutrients. But by rotating crops and strategically positioning cover crops, fields and gardens can fill the soil with greater soil organic matter, often naturally avoiding disease and pest problems.
4. Caution
To minimise physical distancing, regenerative agriculture practitioners often want to be vigilant about chemical activities that can harm soil health. For example, incorrect use of fertilisers and other soil amendments can disrupt the natural connection between plant roots and microorganisms.
Regenerative Agriculture Techniques
These are the regenerative agriculture methods to elaborate its benefits.
1. No-till Regenerative Farming Practices
- No-till farming propagates as it reduces soil erosion and carbon dioxide emissions.
- It helps agronomists to avoid bare soil and thus helps in combating erosion.
- Also include greater soil nutrient retention and availability to crops, less soil crusting, retention and increased water penetration.
2. Annual Organic Cropping
- The organic annual crop method is used for pesticides and non-chemical fertilisers to reduce the negative impact on humans and nature.
- In addition, we have analysed with studies that it is possible without compromising quality and yield.
- Also, it helps accelerate crop productivity with the benefits of healthy biodiverse soils.
3. Composting
- This is a regenerative agriculture technique to restore soil fertility and organic matter, which is a key goal.
- You can drive the composting processes through bacteria, fungi, nematodes, earthworms, and other organisms.
- Moreover, Compost tea is a brewed liquid that supplies soluble nutrients and vital microorganisms for plant growth.
4. Biochar And Terra Preta
- It is a healthier alternative to natural charcoal and is made via farming wastes and burning forestry.
- This explains its ability to manage fertility for a long time and also is of great interest in regenerative agriculture practices.
- in addition, it exceeds its content in the infertile soils of the region up to seventy times.
5. Intensive Agricultural Practices
- Intensive farming practices, soil ecosystems and also include native plants that naturally co-evolved to achieve a balance that could support the vast diversity of plants grown in the same soil.
- In addition, crop rotations that add to the diversity of crops will increase the variety of soil microorganisms and create a soil that ensures crop resilience and optimum yield over time.
6. Animal Integration
- Livestock production has separated physically from crop production in forms like concentrated animal feed operations.
- Moreover, These kinds of operations can result in many challenges, including disposal of animal wastes, animal health, water quality and the risk of contaminating watersheds and aquifers.
Benefits of Regenerative Agriculture
There are advantages of regenerative farming that help to create regenerative farms.
Feed the world:- Small farmers feed the world with less than a quarter of all farmland with the help of regenerative organic farming.
Nurture regenerative agriculture biodiversity:- It is fundamental to food security and agricultural production and a valuable ingredient of environmental conservation.
Preserve traditional knowledge:- The system of indigenous farming reveals important ecological clues for developing regenerative agriculture systems.
Revitalise local economies:- With the help of regenerative agriculture, our experience revitalising local economies that provide better livelihoods is the product of strong business acumen and access to markets.
Thestady
Post a Comment